A common skin condition, hyperpigmentation can cause speckling of the skin or dark patches that appear and spread to different parts of the body. This condition can be frustrating, especially when you’ve been working hard toward blemish-free skin. In less common cases, hyperpigmentation can be the result of an underlying health condition.
The good news is that hyperpigmentation can be treated and prevented through numerous methods. Learn more about hyperpigmentation below and your treatment options for dark spots and discoloration.

What Is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is characterized by dark spots or discolorations on the skin. This condition can appear as small or large patches and can sometimes affect the entire body. It isn’t always related to a medical condition, but it can be a symptom of some ailments, so it’s essential to speak with your doctor if you notice new or spreading spots or discoloration.
You can identify hyperpigmentation by looking for areas on your skin that are darker than the surrounding area. These dark areas are usually a result of the overproduction of melanin, a brown pigment in the skin, which is often linked to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays and certain medications.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
Some of the reasons a person can experience hyperpigmentation include:
- Medications or medical conditions: Certain drugs and medical complications can cause hyperpigmentation. Medicines that are often associated with hyperpigmentation include antibiotics and certain chemotherapy drugs. Health conditions or systematic disorders like cancer or lupus can also increase hyperpigmentation.
- Pregnancy hormones: Women experience a massive surge and fluctuation in various hormones during pregnancy. As their hormone levels change, their bodies may produce more melanin, which can cause hyperpigmentation on the skin.
- Sun exposure: When UV rays hit the surface of your skin, your body produces extra melanin to protect your skin from damage. Excess melanin is why people can tan in the sun, but it can also cause a type of hyperpigmentation called sunspots.
- Skin inflammation: Your skin becomes inflamed after experiencing trauma, including acne breakouts, scrapes, cuts, bug bites and eczema. Your body will try to heal the inflammation by delivering more cells that produce pigment to the injury site. Once your skin heals, you may notice hyperpigmentation in the same area on your skin.
- Addison’s disease: Addison’s disease is a rare medical condition that affects the adrenal gland, sometimes causing the body to produce excess melanin. Hyperpigmentation from this disease is most noticeable in areas where you get the most sun exposure, including the hands, neck and face. Any areas that experience more friction may also become hyperpigmented, including the knees and elbows.
While many of the causes of hyperpigmentation aren’t dangerous, it’s essential to see a doctor when you notice these spots or areas of discoloration. You’ll want to rule out any severe causes of hyperpigmentation and determine the reason for it so you can make the necessary changes in your routine.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are multiple types of hyperpigmentation, which include:
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH is the most common type of hyperpigmentation since the skin is prone to injury or inflammatory reactions often caused by acne, burns, wounds and injuries. The body will produce more pigment-producing cells to heal the skin, which can result in dark spots of discoloration. Acne hyperpigmentation is common among those who experience frequent or severe breakouts. Certain conditions can also inflame the skin. PIH isn’t to be confused with post-inflammatory erythema (PIE), which is another source of dark spots caused by acne.
- Melasma: Melasma is more common among women than men and often occurs during pregnancy. It can also occur from any surge in hormones, sun exposure or genetics. The hormone fluctuations will cause the body to produce more cells responsible for creating pigment, potentially causing hyperpigmentation.
- Sunspots: Excessive sun exposure can create dark sun spots, a kind of hyperpigmentation. While sun spots aren’t inherently cancerous, they can be challenging to distinguish from precancerous spots with a similar appearance. It’s essential to get your skin checked when you notice new spots or blemishes on your skin so your doctor can determine whether they’re cancerous.
If you only have hyperpigmentation on your face and you’ve experienced acne, you can likely deduce the cause of your hyperpigmentation on your own. However, it’s always best to see a dermatologist so that you know the proper route of care to treat the condition. Otherwise, you may find that you spend money on unnecessary treatments that don’t work.
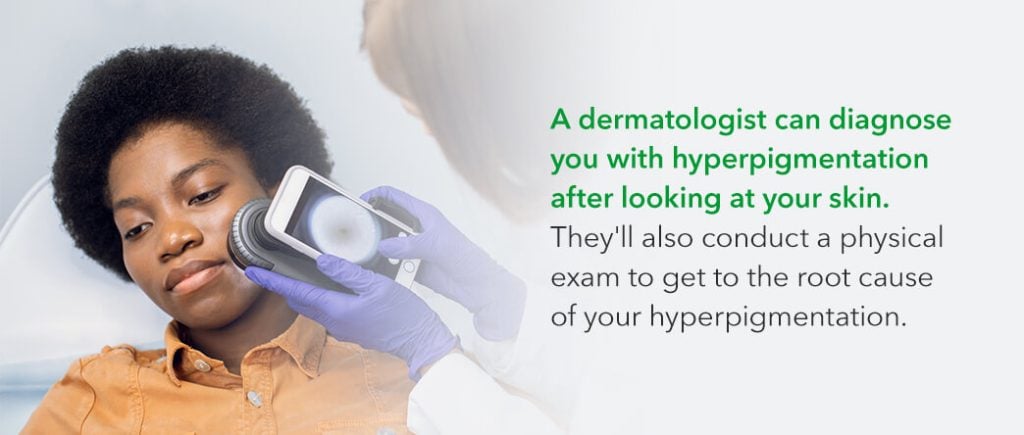
How Is Hyperpigmentation Diagnosed?
A dermatologist can diagnose you with hyperpigmentation after looking at your skin.
During your assessment, the dermatologist will request your medical history to determine if a medical condition or medication is causing the dark spots and discoloration on your skin. They’ll also conduct a physical exam to get to the root cause of your hyperpigmentation.
Expect to answer questions about your lifestyle, too. For example, you may be asked how much time you spend outdoors. These questions will help your dermatologist determine if your hyperpigmentation was caused by sun exposure or something else.
Some cases may require a skin biopsy to get to the cause of your condition. A skin biopsy will remove some cells or a skin sample from the top layer of your skin and send it to a lab to be viewed under a microscope. This procedure allows for an accurate diagnosis so you can receive the correlating treatment.

How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation
While hyperpigmentation is rarely a serious problem, it can affect how a person views themselves and cause problems with confidence. The good news is there are ways to prevent hyperpigmentation and help maintain your natural skin tone.
Here are a few things you can do for hyperpigmentation prevention:
1. Moisturize Your Skin
Your skin has a natural moisture barrier. That said, it can fail to produce enough oil to keep your skin hydrated and encourage cellular turnover or regeneration. If you spend a lot of time in the sun, live in a dry climate or have a dry skin type, your skin may lack the moisture it needs, contributing to hyperpigmentation.
Using a skin care product with additional ingredients, such as retinol or salicylic acid, can help prevent hyperpigmentation by encouraging the growth of healthy cells. Pair that product with a hydrating moisturizer, like one that contains hyaluronic acid, to keep your moisture barrier in top shape.
2. Avoid Messing With Irritated Spots
Inflammation is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation. Popping pimples or scratching at bug bites can cause your skin to become inflamed. Try to stop yourself from picking or scratching at irritants that appear on your skin, or you may risk developing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Instead of messing with spots that may itch, try using acne treatments or a cortisone cream for bug bites. You can talk to a doctor about prescription-strength treatments if skin irritation persists.
3. Consider Your Prescription Medication
As mentioned, some medications can result in discoloration or dark spots. For example, certain birth control medications can cause your hormones to fluctuate, causing an increase in melanin production. The additional pigment can sometimes cause hyperpigmentation.
Prevent hyperpigmentation by researching the medication you’re taking to see if it’s one of the side effects. You can also talk with your doctor to find an alternative drug that doesn’t result in skin discoloration or dark spots.
4. Minimize Sun Damage
Excessive exposure to UV rays can cause you to develop sun spots, a type of hyperpigmentation. While hyperpigmentation is rarely harmful, you still want to protect your skin from discoloration and UV damage.
Always wear a quality sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and wear clothing or hats that block out the sun. If possible, try to stay out of the sun when the sun’s rays are at peak strength, usually midday or between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Stay away from tanning beds since the UV lights can cause the same damage, even though you’re not out in the sun.
Reducing your exposure to the sun will prevent sun damage and, in turn, hyperpigmentation.
5. Use Gentle Skin Care
Certain skin care products can burn or irritate the skin, making it more likely for you to develop hyperpigmentation. If you have melasma or a condition that makes your skin more sensitive, avoiding harsh products is critical. Look for products made for sensitive skin types to prevent inflammation and hyperpigmentation.
Being proactive about your skin’s health can help you reduce or prevent hyperpigmentation.
Effective Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
Once your dermatologist has determined the root cause of your hyperpigmentation, you can begin treatment. The type of treatment you need will vary based on the cause of your condition, but different types of effective treatment for hyperpigmentation include:
- Topical vitamin C: Using a topical vitamin C product under sunscreen every day can help double up your protection against UV rays while blocking the excess pigment production.
- Lightening creams: You can use lightening creams to help reduce pigmentation for individuals with melasma or discoloration. Prescription-strength lightening creams will often include ingredients such as hydroquinone, but those with severe cases may use creams with cortisone or tretinoin.
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels use strong acids to reduce hyperpigmentation. A chemical peel will remove a layer of the epidermis, which helps reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. Talk to your doctor about what’s best for your skin before you schedule a chemical peel appointment.
- Skin resurfacing: Skin resurfacing uses lasers to reduce hyperpigmentation. There are two types of skin resurfacing — nonablative and ablative. Nonablative treatments promote collagen production and skin tightening, while ablative treatments remove a layer of the skin. Each type of treatment encourages cellular regeneration, though ablative skin resurfacing treatments are more potent.
- Dermabrasion or microdermabrasion: Dermabrasion and microdermabrasion use superficial scarring to remove a layer of the epidermis. However, dermabrasion goes one step further and affects a layer of the dermis. Both can reduce hyperpigmentation, but dermabrasion works quickly so that you can see results sooner.
- Intense pulse light therapy (IPL): IPL therapy is a nonablative laser treatment that helps encourage collagen production and reduces pigmentation.
- Retinoids: Retinoids are found in many skin care products and help reduce melanin production. Retinoids can penetrate deep into the layers of your skin, allowing you to treat hyperpigmentation effectively. You can use over-the-counter retinoids or prescription-strength retinoids for a more substantial effect.
- Face acids: Exfoliating your skin with face acids will help eliminate dead and damaged skin cells, allowing new ones to take their place. Face acids will help smooth your skin tone and create an even appearance. Look for products with 10% or less acid in the ingredients list to reduce skin irritation. Common acids you could try include salicylic acid, citric acid, glycolic acid and kojic acid.
Does Hyperpigmentation Go Away?
Hyperpigmentation can go away on its own, depending on the underlying cause. However, it can take some time for the dark spots and discoloration to fade. Severe cases of hyperpigmentation may not disappear completely, even with aggressive treatment. People with darker skin tones may experience more severe hyperpigmentation and longer-lasting cases due to the presence of additional melanin in the skin.
If you have hyperpigmentation, the good news is that it’s rarely ever harmful and usually isn’t an indication of a serious medical condition. Still, it’s a good idea to see a medical professional. Once you know that your hyperpigmentation isn’t the result of a more serious condition, you can find the proper way to treat it and see effective results.
Treat Hyperpigmentation at Synergy Wellness
If you’ve started to notice dark spots or patches of discoloration on your skin, you may have hyperpigmentation. Synergy Wellness can help you find an effective noninvasive treatment that works for you. We offer pico laser treatment for melasma and Lumecca IPL therapy to treat dark spots and correct color imperfections.
These noninvasive treatments allow you to see results with little to no downtime after the procedure. You can get back to living life while improving the appearance of your skin. You’ll also experience minimal side effects, sometimes none at all, allowing you to treat hyperpigmentation without the pain or discomfort of other treatments.
Tackle hyperpigmentation head-on with Synergy Wellness. Contact us today to schedule a consultation.




